Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to evaluate the amount of root canal dentin removed and apical transportation occurrence after instrumentation of mesiobuccal canals of maxillary molars with ProTaper Next (PTN [Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland]), OneShape (OS [MicroMega, Besançon, France]), and EdgeFile (EF [Edge Endo, Albuquerque, NM]) rotary systems.
Methods
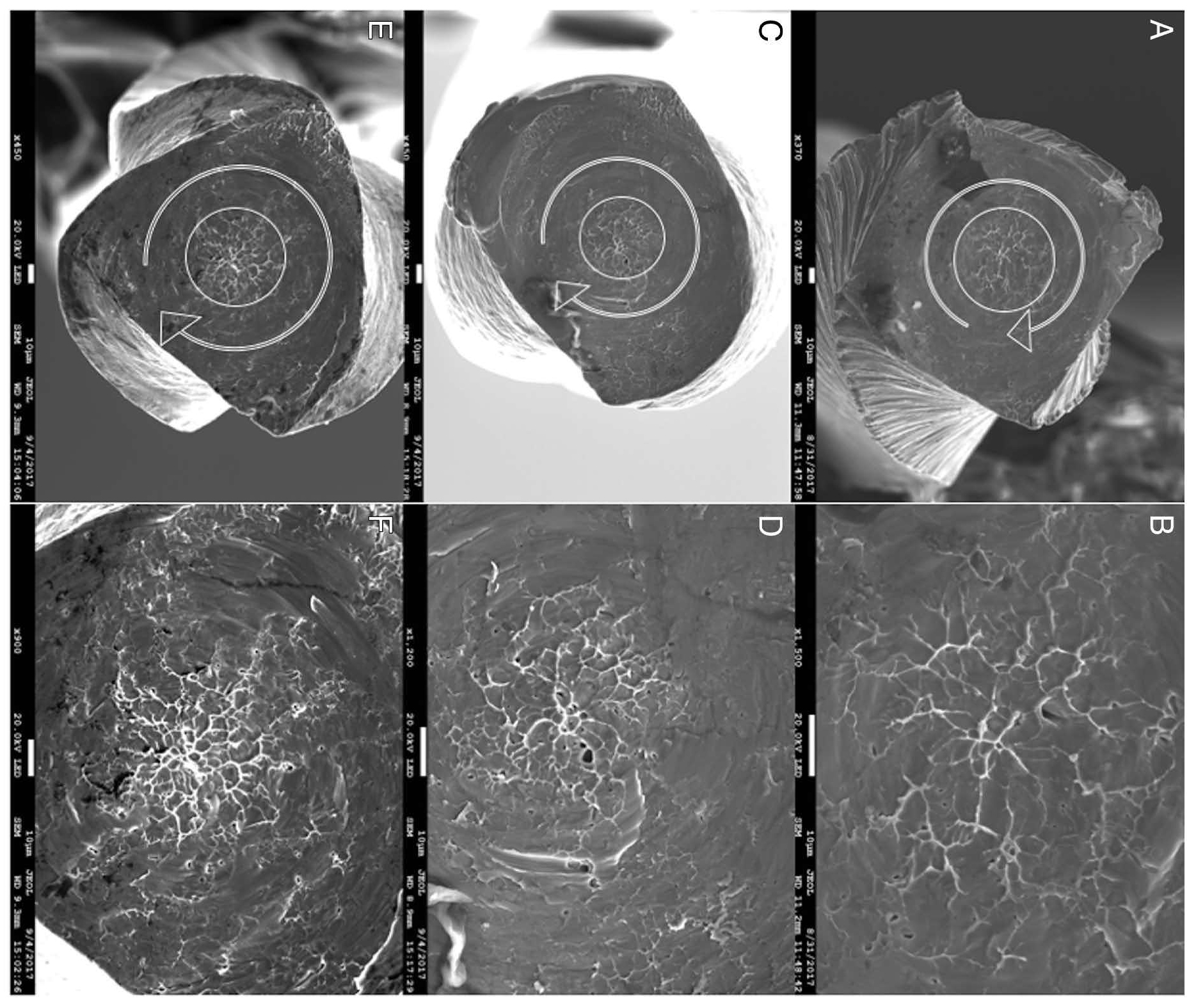
Twenty-seven mesiobuccal canals of maxillary molars were used. Canals were randomly divided into 3 groups for canal preparation: PTN, EF X3, or OS (n = 9 for each group). Micro–computed tomographic imaging was used to measure apical transportation (mm) and the volume of dentin removed (mm3). The amount of dentin removed was measured for the coronal portion and for the whole canal length. Superposition of pre- and postoperative cross-sectional apical slices were used to measure apical transportation at 1 mm from the apex; the differences were evaluated using the Kruskal-Wallis test and Wilcoxon analysis. The Spearman correlation coefficient was used to display the relationship between variables for each group. The significance level was set at P < .05.
Results
The percentages of the amount of dentin removed on the coronal portion and the amount removed for the whole canal length were statistically similar between groups (P > .05). The average amount of apical transportation for the PTN, OS, and EF X3 were 0.197, 0.263, and 0.218 mm, respectively. Statistically, there were no significant differences between the 3 rotary instruments for apical transportation.
Conclusions
The amount of dentin removed for the coronal third portion and the whole canal length was similar for the PTN, OS, and EF X3 rotary instruments. Although there were differences in the sizes of apical enlargement, no apical transportation was observed in any of the instrumentation systems.